섬나라 아일랜드(BFS) + DFS 방식으로 풀기
문제
설명
N*N의 섬나라 아일랜드의 지도가 격자판의 정보로 주어집니다.
각 섬은 1로 표시되어 상하좌우와 대각선으로 연결되어 있으며, 0은 바다입니다.
섬나라 아일랜드에 몇 개의 섬이 있는지 구하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
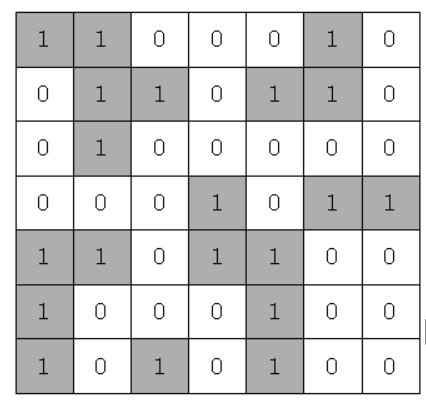
만약 위와 같다면 섬의 개수는 5개입니다.
입력
첫 번째 줄에 자연수 N(3<=N<=20)이 주어집니다.
두 번째 줄부터 격자판 정보가 주어진다.
출력
첫 번째 줄에 섬의 개수를 출력한다.
예시 입력 1
7
1 1 0 0 0 1 0
0 1 1 0 1 1 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 1 0 1 0 0
예시 출력 1
5
해결방법
- DFS를 수행할 때와 BFS 수행할 때의 차이를 알자.
- 다음 수행을 큐로 체크하면서 계속 동일 레벨에서 -> 현재에서 체크할 수 있는 끝까지 가는 경우 -> BFS
- 다음 수행을 함수 재귀형태로 체크 -> 계속 넘어가기만 함 -> DFS
- 다음 갈 곳을 체크 해야 하는데, 이게 8방향으로 이루어 진다.
코드
// DFS
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int answer = 0, n;
static int[] dx = {-1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1};
static int[] dy = {0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1};
public void DFS(int x, int y, int[][] board) {
// 8방향 체크 -> 1이 있는 곳으로 뻗는다. 가다가 갈데가 없으면 종료됨.
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < n && board[nx][ny] == 1) {
board[nx][ny] = 0;
DFS(nx, ny, board);
}
}
}
public void solution(int[][] board) {
// 이중 for문을 돌면서 DFS 수행.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// 1(육지)를 만난다? 정답 추가하고 0으로 바꾸고 바로 DFS 수행
if (board[i][j] == 1) {
answer++;
board[i][j] = 0;
// 돌기 시작
DFS(i, j, board);
// 다 돌면 (갈데 없으면 리턴하는 곳)
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main T = new Main();
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
n = kb.nextInt();
int[][] arr = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
arr[i][j] = kb.nextInt();
}
}
T.solution(arr);
System.out.println(answer);
}
}
// BFS
import java.util.*;
class Point {
int x, y;
Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
class Main {
static int answer = 0, n;
static int[] dx = {-1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1};
static int[] dy = {0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1};
Queue<Point> queue = new LinkedList<>();
public void BFS(int x, int y, int[][] board) {
queue.add(new Point(x, y));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Point pos = queue.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int nx = pos.x + dx[i];
int ny = pos.y + dy[i];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < n && board[nx][ny] == 1) {
board[nx][ny] = 0;
queue.add(new Point(nx, ny));
}
}
}
}
public void solution(int[][] board) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 1) {
answer++;
board[i][j] = 0;
BFS(i, j, board);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main.Main T = new Main.Main();
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
n = kb.nextInt();
int[][] arr = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
arr[i][j] = kb.nextInt();
}
}
T.solution(arr);
System.out.println(answer);
}
}
